基于NAO机器人的目标识别与抓取(任务书,开题报告,论文说明书15000字,代码)
摘要
机器人作为近年来备受各大研究机构青睐的高级平台,涵盖了计算机技术,人工智能,控制技术,仿生学多个学科,体现着一个国家高技术水平和现代化程度。机器人的快速发展与成熟更是直接推动了工业的自动化进程。视觉系统是机器人感知外部环境的重要信息渠道,拥有多自由度机械臂的机器人控制系统是仿人机器人的重要组成,也是机器人进行操作的执行结构。通过融合视觉系统与控制系统组成视觉伺服,允许机器人自主智能与外界环境进行实时交互是如今机器人技术的重要热点内容。
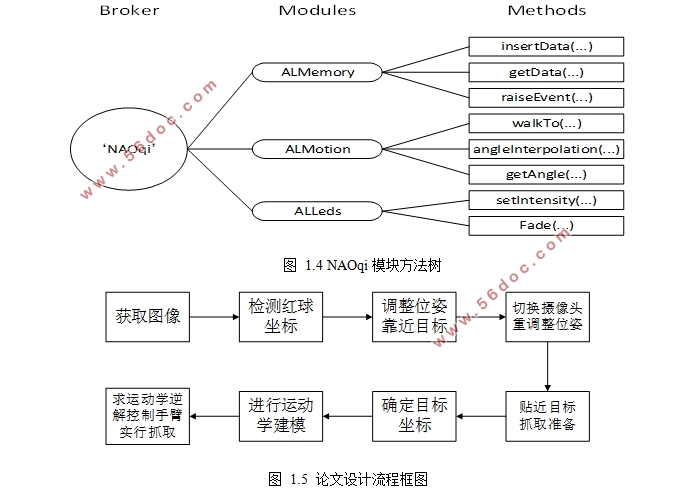
本文基于NAO机器人平台,完成对指定颜色小球的识别和对目标小球的抓取。第一步,利用NAO机器人的视觉系统,从外部环境中识别出指定颜色的目标小球,并且返回目标的位姿信息。在对目标识别以后,机器人自动跟踪目标,将人和球的间距控制在合适的大小,方便进行抓取,最后在适当的距离下,通过位置信息控制机器人的特定手臂实现对特定颜色小球的抓取操作。
针对目标小球的识别模块,其核心是图像处理。本文首先根据NAO机器人摄像头获取的图像,首先对获取的图像按目标颜色进行颜色分割,再对分割后的图像进行滤波、去噪等操作,消除其他外界干扰影响目标小球的识别,分离出指定颜色。再对分离后的图像通过霍夫圆变换检测,识别目标颜色的小球,恢复后得到目标颜色小球的信息。通过对图像的处理,获取到机器人相对于目标的距离,根据距离选择执行跟踪操作或者抓取操作。
针对NAO机器人的手臂控制,本文通过MATLAB的robotic toolbox工具箱实现了对机器人手臂的三个主要自由度进行D-H运动学建模,通过对目标小球相对机器人的三维空间坐标求取运动学逆解来控制机器人手臂移动到目标小球处,再通过设置关节角度使末端执行器的手爪闭合来实现小球的抓取操作,仿真结果表明,该方法有效的完成了对机器人手臂的控制。
关键字:NAO机器人;目标识别;运动学;霍夫圆变换;
Abstract
As a high-level platform which has been favored by major research institutions in recent years, robot has covered many disciplines of computer technology, artificial intelligence, control technology and bionics, which embodies a country's high-tech level and modernization. The rapid development and maturity of the robot is a direct promotion of the industrial automation process. The visual system is an important information channel for robot to perceive the external environment. The robot control system with multi-degree of freedom robot is an important component of humanoid robot, and it is also the execution structure of robot operation. Through the integration of visual systems and control systems composed of visual servo, robot intelligent and real-time interaction with the external environment is now an important hotspot of robot technology content.
Based on the NAO robot platform, this paper completes the identification and the crawling of the specified colored ball. First, the NAO robot's visual system is used to identify the target of the specified color from the surrounding environment and obtain the relevant pose information of the target. After the target recognition, the robot automatically tracks the target, controls the distance between the person and the ball in the appropriate size in order to crawling more convenient. Finally at the appropriate distance, according the position information to control the robot specific arm to grab the specific color ball.
For the target ball recognition module, its core is image processing. In this paper, firstly, according to the image acquired by the NAO robot camera, the image is first divided according to the target color, and then the divided image is filtered and de-noised. The other external disturbance is affected by the identification of the target ball.The separated image is detected by the Hough circle transformation to identify the target color of the ball, getting the target color ball information afterimagerecovery. Through the processing of the image, the distance of the robot relative to the target is acquired, and the tracking operation or the crawling operation is performed according to the distance selection.
The kinematic inverse solution is obtained by the three-dimensional spatial coordinates of the target ball relative to the robot, and then control robot arm moves to the target ball. Setting the joint angle so that the end of the handle of the claws closed to achieve the crawling operation of the ball. The simulation results show that the method can effectively control the robot arm.
Keywords: NAO robot; Target Recognition; Kinematics; Hough circle transformation;


目录
摘要
Abstract
第1章绪论
1.1 研究背景及意义
1.2国内外研究现状
1.3 NAO机器人介绍
1.3.1 NAO机器人硬件系统
1.3.2 NAO机器人软件配置
1.4 本文研究内容与组织结构
第2章图像处理与目标识别
2.1 NAO视觉系统
2.2颜色空间选择
2.3 图像预处理
2.3.1 图像分割
2.3.2图像滤波、去噪
2.4 霍夫圆变换
2.5 目标定位
2.6 本章小结
第3章目标抓取
3.1 NAO机械臂
3.2正向运动学建模
3.3 逆向运动学求解
3.4 运动学仿真
3.5抓取过程设置
3.6 实验结果与分析
3.7 本章小结
第4章总结与展望
4.1总结
4.2展望
参考文献
致谢
|