高氮微合金钢轧制组织与性能的研究
来源:56doc.com 资料编号:5D4353 资料等级:★★★★★ %E8%B5%84%E6%96%99%E7%BC%96%E5%8F%B7%EF%BC%9A5D4353
资料以网页介绍的为准,下载后不会有水印.资料仅供学习参考之用. 密 保 惠 帮助
资料介绍
摘要:通过对高氮微合金钢轧制组织与性能的研究,探讨了高氮微合金钢轧制组织与性能的关系,为更好地提高试样钢的性能与改善组织提供了试验依据。通过拉伸、冲击测试,对其性能进行分析;再对该钢试样表面磨制、抛光后,用4%硝酸酒精溶液进行腐蚀,用光学显微镜进行观察并对其晶粒度和铁素体转变量的测定;另外再对打磨好的该钢试样进行扫描电镜和透射电镜观察形貌组织观察,比较钢中显微组织的特点,确定了第二相粒子的存在。结果表明,轧制后的钢与普通16Mn钢相比,屈服强度和抗拉强度都有所提高,第二相粒子起沉淀强化作用。
关键词:微合金钒氮钢;珠光体;细晶强化;第二相粒子
Study on Rolling Microstructure and Properties of High Nitrogen Microalloyed Steels
Abstract:Through the research on the microstructure and propertiesthe of high nitrogen-rolling steel,we discuss on the high nitrogen-rolling steel microstructure and properties of relations,which provides experimental bases for improving the performance
of steel specimens and improve the microstructure. And the properties are analyzed by tensile test and impact test. After grinding and polishing of the pecimen surface, and corrupting by 4% nitric acid alcohol solition, the microstructure of high nitrogen microalloyed steels are observed by light microscope, its grain size and transformation quantity of ferrites are tested.Besides, with the help of scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope,the polished steels are observed. Through compared with the characteristic of microstructures of steels, the secondary phase particles existence have been determined.The results show, compared with ordinary 16 Mn steel, both the yield strength and tensile strength of rolling steel have been raised.It is because of the second phase particles precipitation enhancement.
Key words:microalloyed vanadium nitrogen steels; pearlite;fine crystal strengthening; the secondary phase particles.
通过对高氮微合金钢轧制组织与性能的研究,得出如下结论:
a) 试验钢的基本组织为铁素体+珠光体,轧制后呈带状珠光体。
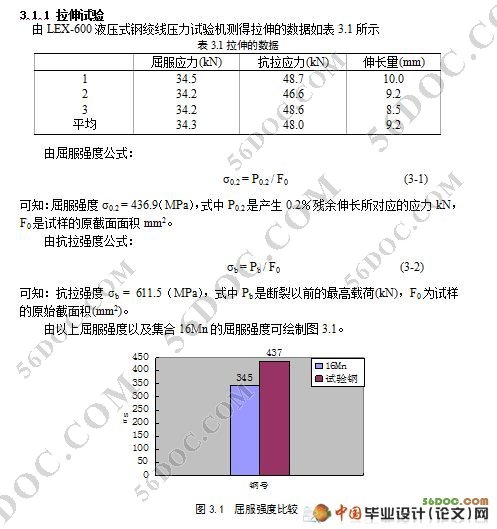
b) 试验钢的屈服强度和抗拉强度都比同类钢(如16Mn钢)都优越。
c) 试验钢的冲击韧性与同类钢(如16Mn钢)相比也明显提高。
d) 通过SEM和TEM对试验钢的形貌观察,确定了第二相粒子V(C、N)的存在。
e) 试验钢的强化机制为细晶强化和沉淀强化。
目 录 16000字
摘要....Ⅰ
Abstract...Ⅱ
1 绪论 1
1.1 合金钢 1
1.2 合金结构钢 1
1.2.1 普通低合金结构钢 1
1.2.2 机械制造用合金结构钢 2
1.3 微合金钢 2
1.4 钒微合金化结构钢的发展 3
1.5 合金元素对珠光体转变的影响 4
1.5.1 合金元素对珠光体转变时碳化物形成的影响 4
1.5.2 合金元素对珠光体转变时γ-α相变的影响 6
1.5.3 合金元素对淬透性的影响 6
1.6 实验的目的和意义 7
2 试验设备及实验方法 8
2.1 原材料及实验仪器、设备 8
2.2 试样的制备 8
2.2.1 试验钢成分及取样部位 8
2.2.2 试验钢轧制工艺参数 9
2.3 机械性能测试 9
2.4 显微组织观察与测试 10
2.4.1金相显微组织观察 10
2.4.2 晶粒度的测定 10
2.4.3 扫描电镜组织的形貌观察 10
2.4.4 透射电镜组织形貌观察 10
2.5试验钢强化增量计算 11
3 结果与分析 12
3.1 机械性能测试 12
3.1.1 拉伸试样 12
3.1.2冲击试样 13
3.2 金相组织图片 14
3.3 扫描电镜形貌观察 16
3.4透射电镜组织形貌观察 18
3.4.1 透射电镜组织形貌观察 18
3.4.2 显微组织的回复. 18
4 讨论 20
4.1影响屈服强度的因素 20
4.1.1 金属的本身对屈服强度的影响 20
4.1.2 晶粒大小的影响 20
4.1.3 固溶强化 20
4.1.4第二相粒子的影响 20
4.1.5形变强化 21
4.1.6温度及变形速度 21
4.2 V、N的主要作用 21
4.2.1 V的作用 21
4.2.2 N的作用 21
4.2.3 V、N合金的强化作用 21
结 论 23
参考文献 24
致 谢 25
|

